Activity: SQL basics
(no submission)Purpose:
- Be familiar with database queries
- Practice writing and interpreting SQL
- Verify that you have access to the database server and the database server works properly
- Get ready to work on homework assignment and course project
You may make a copy of a activity-sql-basic.sql and complete this activity or type your queries directly in your database environment and export the .sql file later.
You may work alone or with 3-4 other students in this course (max size=5).
Let's warm up
- Create a table
CREATE TABLE my_todo (id INT, task VARCHAR(20), priority VARCHAR(10), PRIMARY KEY (id)); - Insert data into a table
INSERT INTO my_todo VALUES (99, "read book", "low"); INSERT INTO my_todo VALUES (101, 'do homework 2', "normal"); INSERT INTO my_todo VALUES (212, "write sql", "high"); INSERT INTO my_todo VALUES (114, "practice", "normal");
- Retrieve data
SELECT * FROM my_todo;
SELECT * FROM my_todo WHERE priority="high";
SELECT * FROM my_todo WHERE priority='normal';
SELECT task FROM my_todo WHERE priority="normal";
SELECT * FROM my_todo WHERE task LIKE "%sql" OR priority = "low";
SELECT DISTINCT * FROM my_todo;
SELECT DISTINCT priority, task FROM my_todo;
SELECT DISTINCT priority FROM my_todo;
- Update data
UPDATE my_todo SET priority="low";
UPDATE my_todo SET priority="high" where task="write sql";
UPDATE my_todo SET priority="normal" where task="do homework 2";
- Delete data
DELETE FROM my_todo WHERE task="do homework 2";
DELETE FROM my_todo;
- Drop a table
DROP TABLE my_todo;
Import alldbs.sql into your database server. Write SQL queries to solve the following problems. You will need to consider tables: loan, depositor, borrower, and account. (Sample data of these tables are also included at the end of this activity for your convenience)
- Find all loans over $1200
SELECT * FROM loan
WHERE amount > 1200;
- Find the loan number for each loan of an amount greater than $1200
SELECT loan_number FROM loan
WHERE amount > 1200;
- Which branches have loan amounts greater than $1200?
SELECT DISTINCT branch_name FROM loan
WHERE amount > 1200;
- List the branches that have loan amounts greater than $1200 in alphabetical order
SELECT DISTINCT branch_name FROM loan
WHERE amount > 1200
ORDER BY branch_name;
- I need the account numbers and balances of all our customers
SELECT account_number, balance FROM account;
- Suppose the bank is updating the customers' account balances with 2.5% interest;
that is, if the customer currently has $100 in his/her account,
the balance will be updated to $100 * 1.025 = $102.5.
Display account numbers and the balances with 2.5% interest of all customers.
Also, rename the column header for balances as "New Balance"
SELECT account_number, balance * 1.025 AS 'New Balance' FROM account;
- Display the names of our customers, the branches they have accounts,
and the amounts they have in their accounts. List them by the branches and then the amounts
SELECT D.customer_name, A.branch_name, A.balance
FROM account A, depositor D
WHERE A.account_number = D.account_number
ORDER BY A.branch_name, A.balance;
- Show me a list of customer names and the amounts they borrowed
SELECT borrower.customer_name, loan.amount FROM borrower, loan
WHERE borrower.loan_number = loan.loan_number;
-- Another solution: (more join later)
SELECT borrower.customer_name, loan.amount FROM borrower NATURAL JOIN loan;
- Give me the names of all customers who have a loan at the Perryridge branch
SELECT DISTINCT customer_name FROM borrower, loan
WHERE loan.branch_name = "Perryridge" AND borrower.loan_number = loan.loan_number;
-- Another solution: (more join later)
SELECT DISTINCT customer_name FROM borrower NATURAL JOIN loan
WHERE loan.branch_name = "Perryridge"
- Find the names of all customers, their loan numbers,
the branch they have their loan with, and the amount of their loan.
Note: do not list the common column(s) twice
SELECT customer_name, borrower.loan_number, branch_name, loan.amount from borrower, loan
WHERE borrower.loan_number = loan.loan_number; - [optional] Find the names of all customers who have a loan, an account, or both from the bank
(SELECT customer_name FROM depositor)
UNION
(SELECT customer_name FROM borrower);
- [optional] Find the names of all customers who have a loan and an account from the bank
(SELECT customer_name FROM depositor)
INTERSECT
(SELECT customer_name FROM borrower);
-- Another solution: (more join later)
SELECT DISTINCT customer_name FROM depositor NATURAL JOIN borrower;
Table: account
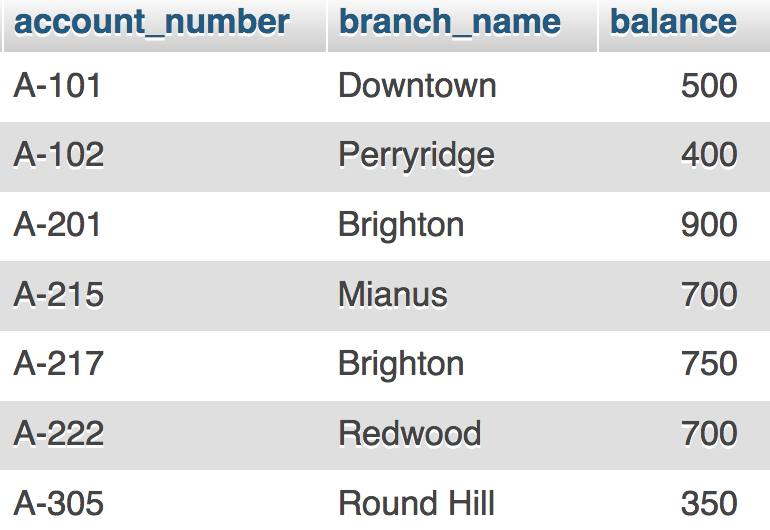

Table: depositor
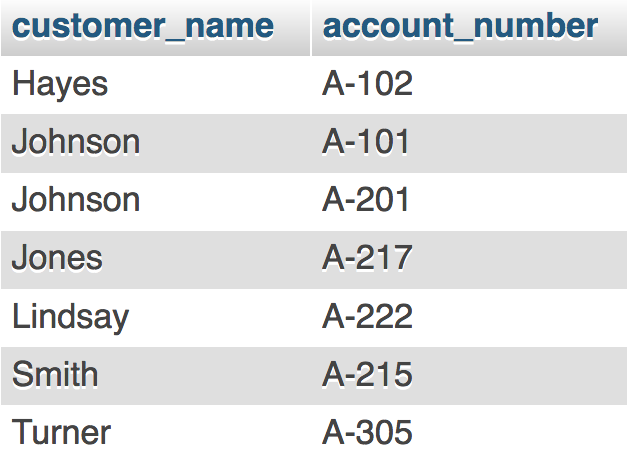

Table: loan
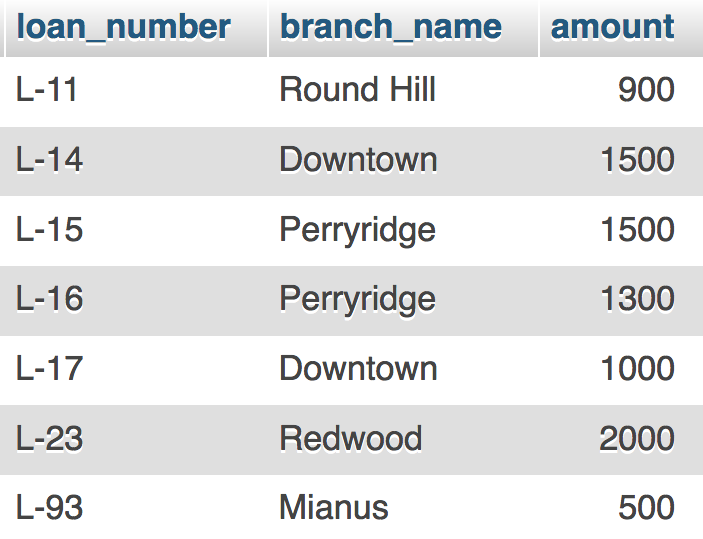

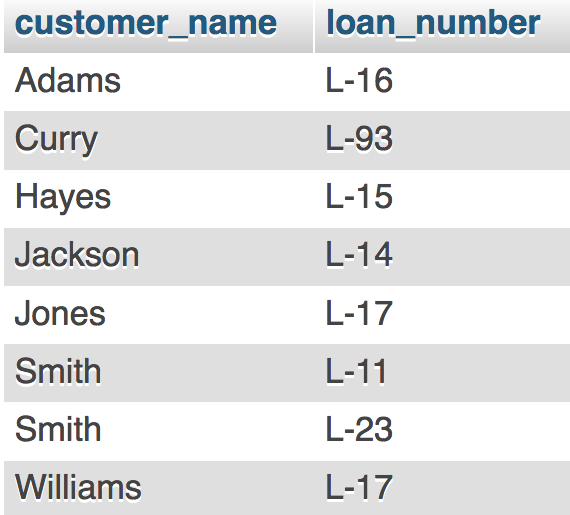
Table: borrower

Copyright © 2024 Upsorn Praphamontripong
Released under the
 CC-BY-NC-SA 4.0 license.
CC-BY-NC-SA 4.0 license.