stack X
Activity: IDM and ISP criteria — GenericStack
(no submission)Purpose: Understand and practice ISP coverage criteria
You may make a copy of a worksheet and complete this activity, or simply type your answers in any text editor.
You may work alone or with at most two other students in this course.
Task 1: Model input domain (refer to POTD 2: IDM GenericStack)
This is from exercise 6.1, #4 (AO textbook).
Derive input space partitioning test inputs for the GenericStack class
with the following method signatures:
public GenericStack ();public void push (Object X);public Object pop ();public boolean isEmpty ();
Assume the usual semantics for the GenericStack.
Try to keep your partitioning simple and choose a small number of partitions and blocks.
- List all of the input variables, including the state variables
sample solution
- Define characteristics of the input variables. Make sure you cover all input variables
sample solutionNote: (these are only some possible characteristics) There are 4 testable units here (the constructor and the three methods); there is substantial overlap between the characteristics relevant for each other. For the three methods, the implicit parameter is the state of the GenericStack. The only explicit input is the Object x parameter in Push(). The constructor has neither inputs nor implicit parameters. Typical characteristics for the implicit state are: C1: the size of the stack C2: whether the stack contains null entries Typical characteristics for Object X is: C3: whether X is null There are also characteristics that involves the combination of Object X and the stack state. C4: does Object X appear in the stack?
- Partition the characteristics into blocks
sample solutionC1: the size of the stack b1 = 0 | b2 = 1 | b3 > 1 C2: whether the stack contains null entries b1 = true | b2 = false C3: whether X is null b1 = true | b2 = false C4: does Object X appear in the stack? b1 = true | b2 = false
- Define values for each block
sample solution(possible values can be anything that fits the characteristic and block constraint) C1: the size of the stack stack = [] | stack = ["cat"] or [null] | stack = ["cat", "dog"] or ["cat", null] or ["cat", "dog", "ox"] C2: whether the stack contains null entries stack = [null] or [null, "cat", null] | stack = ["cat", "dog"] or ["cat", "dog", "ox"] C3: whether X is null X = null | X = "cat" or "dog" or "" C4: does Object X appear in the stack? ( null, [null, "cat", null] ) or ("cat", ["cat", "dog"] ) | ( null, ["cat"] ) or ("cat", ["dog", "ox"] )
Task 2: Choose combinations of values
- Apply All Combination Coverage (ACoC)
- Compute the (maximum) number of tests
sample solution
#tests = 3 * 2 * 2 * 2 = 24
- Derive test requirements
sample solution
For simplicity, let's rename the blocks in Task 1, question 3. C1: [C11, C12, C13] C2: [C21, C22] C3: [C31, C32] C4: [C41, C42] TR = { (C11,C21,C31,C41), (C11,C21,C31,C42), (C11,C21,C32,C41), (C11,C21,C32,C42), (C11,C22,C31,C41), (C11,C22,C31,C42), (C11,C22,C32,C41), (C11,C22,C32,C42), (C12,C21,C31,C41), (C12,C21,C31,C42), (C12,C21,C32,C41), (C12,C21,C32,C42), (C12,C22,C31,C41), (C12,C22,C31,C42), (C12,C22,C32,C41), (C12,C22,C32,C42), (C13,C21,C31,C41), (C13,C21,C31,C42), (C13,C21,C32,C41), (C13,C21,C32,C42), (C13,C22,C31,C41), (C13,C22,C31,C42), (C13,C22,C32,C41), (C13,C22,C32,C42) } Analyze and remove any infeasible test requirements C11: an empty stack, C21: stack contains null -- conflict, thus remove all test requirements that have C11 and C21 C11: an empty stack, C41: X appears in the stack -- conflict, thus remove all test requirements that have C11 and C41 C12: stack of size 1, C21: stack contains null, C32: X is not null, C41: X is in stack -- cannot have a stack of size 1 that contains a null entry, X in a stack but X is not null, thus remove a test requirement (C12, C21, C32, C41) C12: stack of size 1, C22: stack does not contain null, C31: X is null, C41: X is in stack -- cannot have a stack of size 1 that does not contain a null entry, but X is null and is in a stack, thus remove a test requirement (C12, C22, C32, C41) C21: stack contains null, C31: X is null, C42: X is not in stack -- if a stack contains a null, X is null, X must appear in a stack thus remove all test requirements with C21, C31, C42 C22: stack does not contain null, C31: X is null, C41: X is in stack -- cannot have a stack that does not contain null, but X is null and is in a stack thus remove all test requirements with C22, C31, C41 TR = { (C11,C21,C31,C41), (C11,C21,C31,C42), (C11,C21,C32,C41), (C11,C21,C32,C42), (C11,C22,C31,C41), (C11,C22,C31,C42), (C11,C22,C32,C41), (C11,C22,C32,C42), (C12,C21,C31,C41), (C12,C21,C31,C42), (C12,C21,C32,C41), (C12,C21,C32,C42), (C12,C22,C31,C41), (C12,C22,C31,C42), (C12,C22,C32,C41), (C12,C22,C32,C42), (C13,C21,C31,C41), (C13,C21,C31,C42), (C13,C21,C32,C41), (C13,C21,C32,C42), (C13,C22,C31,C41), (C13,C22,C31,C42), (C13,C22,C32,C41), (C13,C22,C32,C42) } - Substitute test input values
sample solution
Use the values defined in Task 1, question 4. Revise and update the values as needed. (C11,C22,C31,C42) --> (X=null, stack=[]) (C11,C22,C32,C42) --> (X="cat", stack=[]) (C12,C21,C31,C41) --> (X=null, stack=[null]) (C12,C21,C32,C42) --> (X="cat", stack=[null]) (C12,C22,C31,C42) --> (X=null, stack=["cat"]) (C12,C22,C32,C41) --> (X="cat", stack=["cat"]) (C12,C22,C32,C42) --> (X="dog", stack=["cat"]) (C13,C21,C31,C41) --> (X=null, stack=["cat", null]) (C13,C21,C32,C41) --> (X="cat", stack=["cat", null]) (C13,C21,C32,C42) --> (X="dog", stack=["cat", null]) (C13,C22,C31,C42) --> (X=null, stack=["cat", "dog"]) (C13,C22,C32,C41) --> (X="cat", stack=["cat", "dog"]) (C13,C22,C32,C42) --> (X="bird", stack=["cat", "dog"])
- Compute the (maximum) number of tests
- Apply Each Choice Coverage (ECC)
- Compute the (maximum) number of tests
sample solution
#tests = max_#blocks = 3
- Derive test requirements
sample solution
TR = { (C11,C22,C32,C42), (C12,C21,C31,C41), (C13,C22,C32,C42) } - Substitute test input values
sample solution
(C11,C22,C32,C42) --> (X="cat", stack=[]) (C12,C21,C31,C41) --> (X=null, stack=[null]) (C13,C22,C32,C42) --> (X="bird", stack=["cat", "dog"])
- Compute the (maximum) number of tests
- Apply Pair-Wise Coverage (PWC)
- Compute the (maximum) number of tests
sample solution
#test = 1st_max_#block * 2nd_max_#block = 3 * 2 = 6
- Derive test requirements
sample solution
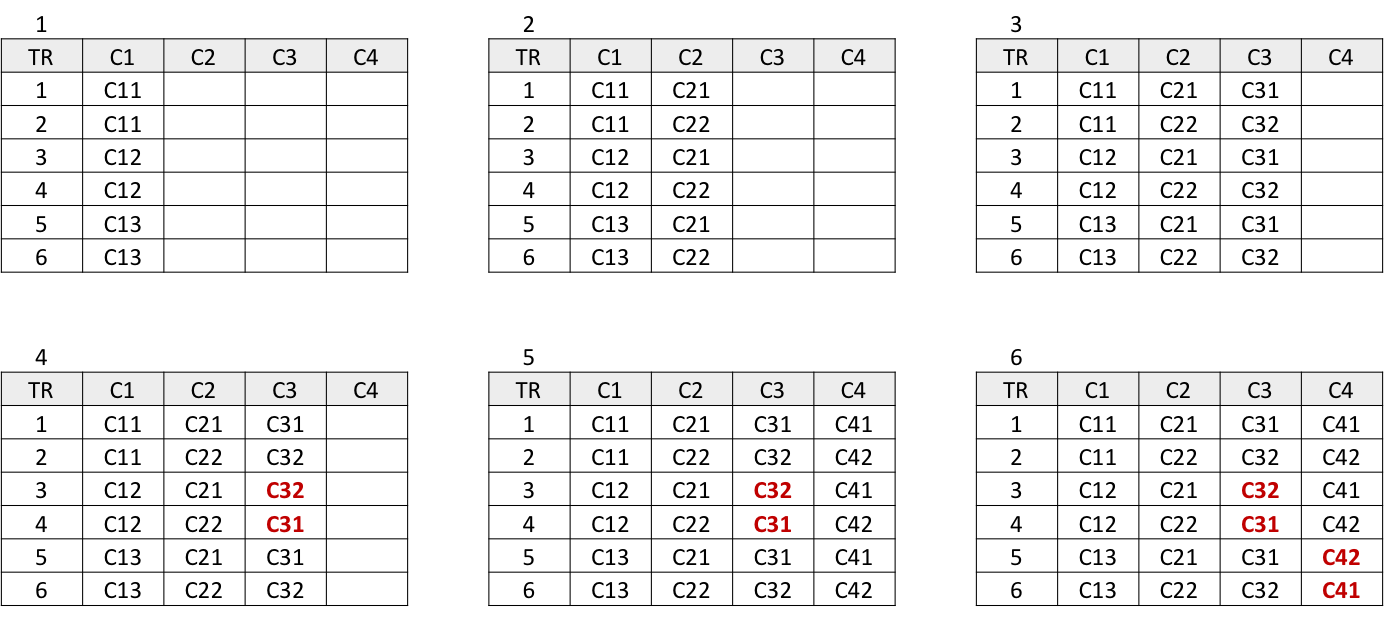 TR = { (C11,C21,C31,C41), (C11,C22,C32,C42), (C12,C21,C32,C41),
(C12,C22,C31,C42), (C13,C21,C31,C42), (C13,C22,C32,C41) }
Analyze and remove any infeasible test requirements
C11: an empty stack, C21: stack contains null
-- conflict, thus remove all test requirements that have C11 and C21
C12: stack of size 1, C21: stack contains null, C32: X is not null, C41: X is in stack
-- cannot have a stack of size 1 that contains a null entry, X in a stack but X is not null,
thus remove a test requirement (C12, C21, C32, C41)
C21: stack contains null, C31: X is null, C42: X is not in stack
-- if a stack contains a null, X is null, X must appear in a stack
thus remove all test requirements with C21, C31, C42
TR = { (C11,C21,C31,C41), (C11,C22,C32,C42), (C12,C21,C32,C41),
(C12,C22,C31,C42), (C13,C21,C31,C42), (C13,C22,C32,C41) }
TR = { (C11,C21,C31,C41), (C11,C22,C32,C42), (C12,C21,C32,C41),
(C12,C22,C31,C42), (C13,C21,C31,C42), (C13,C22,C32,C41) }
Analyze and remove any infeasible test requirements
C11: an empty stack, C21: stack contains null
-- conflict, thus remove all test requirements that have C11 and C21
C12: stack of size 1, C21: stack contains null, C32: X is not null, C41: X is in stack
-- cannot have a stack of size 1 that contains a null entry, X in a stack but X is not null,
thus remove a test requirement (C12, C21, C32, C41)
C21: stack contains null, C31: X is null, C42: X is not in stack
-- if a stack contains a null, X is null, X must appear in a stack
thus remove all test requirements with C21, C31, C42
TR = { (C11,C21,C31,C41), (C11,C22,C32,C42), (C12,C21,C32,C41),
(C12,C22,C31,C42), (C13,C21,C31,C42), (C13,C22,C32,C41) }
- Substitute test input values
sample solution
(C11,C22,C32,C42) --> (X="cat", stack=[]) (C12,C22,C31,C42) --> (X=null, stack=["cat"]) (C13,C22,C32,C41) --> (X="cat", stack=["cat", "dog"])
- Compute the (maximum) number of tests
- Apply Base Choice Coverage (BCC)
- Compute the (maximum) number of tests
sample solution
#tests = 1(for #base) + ( (3-1) + (2-1) + (2-1) + (2-1) ) = 6
- Derive test requirements
sample solution
First, pick a base. Suppose a base is (C13,C22,C32,C41) Derive the remaining test requirements. Hold all but one base choice constant, use each non-base choice in each other characteristic. C13,C22,C32,C42 C13,C22,C31,C41 C13,C21,C32,C41 C12,C22,C32,C41 C11,C22,C32,C41 TR = { (C13,C22,C32,C41), (C13,C22,C32,C42), (C13,C22,C31,C41), (C13,C21,C32,C41), (C12,C22,C32,C41), (C11,C22,C32,C41) } Analyze and remove any infeasible test requirements C11: an empty stack, C41: X appears in the stack -- conflict, thus remove all test requirements that have C11 and C41 C22: stack does not contain null, C31: X is null, C41: X is in stack -- cannot have a stack that does not contain null, but X is null and is in a stack thus remove all test requirements with C22, C31, C41 TR = { (C13,C22,C32,C41), (C13,C22,C32,C42), (C13,C22,C31,C41), (C13,C21,C32,C41), (C12,C22,C32,C41), (C11,C22,C32,C41) } - Substitute test input values
sample solution
(C13,C22,C32,C41) --> (X="cat", stack=["cat", "dog"]) (C13,C22,C32,C42) --> (X="bird", stack=["cat", "dog"]) (C13,C21,C32,C41) --> (X="cat", stack=["cat", null]) (C12,C22,C32,C41) --> (X="cat", stack=["cat"])
- Compute the (maximum) number of tests
- Apply Multiple Base Choice Coverage (MBCC)
- Compute the (maximum) number of tests
sample solution
Suppose there are 2 base tests: (C13,C22,C32,C41) and (C12,C22,C32,C42) #tests = #base + ( #base*(3-#base_choiceC1) + #base*(2-#base_choiceC2) + #base*(2-#base_choiceC3) + + #base*(2-#base_choiceC4) ) = 2 + ( 2*(3-2) + 2*(2-1) + 2*(2-1) + 2*(2-2) ) = 8 - Derive test requirements
sample solution
Hold all but one base choice constant for each base test, use each non-base choice in each other characteristic. For base test (C13,C22,C32,C41) C13,C22,C32,-- Cannot replace C4 characteristic (all block are used as base choice) C13,C22,C31,C41 C13,C21,C32,C41 C11,C22,C32,C41 For base test (C12,C22,C32,C42) C12,C22,C32,-- Cannot replace C4 characteristic (all block are used as base choice) C12,C22,C31,C42 C12,C21,C32,C42 C11,C22,C32,C42 TR = { (C13,C22,C32,C41), (C13,C22,C31,C41), (C13,C21,C32,C41), (C11,C22,C32,C41), (C12,C22,C32,C42), (C12,C22,C31,C42), (C12,C21,C32,C42), (C11,C22,C32,C42) } Analyze and remove any infeasible test requirements C22: stack does not contain null, C31: X is null, C41: X is in stack -- cannot have a stack that does not contain null, but X is null and is in a stack thus remove all test requirements with C22, C31, C41 C11: an empty stack, C41: X appears in the stack -- conflict, thus remove all test requirements that have C11 and C41 TR = { (C13,C22,C32,C41), (C13,C22,C31,C41), (C13,C21,C32,C41), (C11,C22,C32,C41), (C12,C22,C32,C42), (C12,C22,C31,C42), (C12,C21,C32,C42), (C11,C22,C32,C42) } - Substitute test input values
sample solution
(C13,C22,C32,C41) --> (X="cat", stack=["cat", "dog"]) (C13,C21,C32,C41) --> (X="cat", stack=["cat", null]) (C12,C22,C32,C42) --> (X="dog", stack=["cat"]) (C12,C22,C31,C42) --> (X=null, stack=["cat"]) (C12,C21,C32,C42) --> (X="cat", stack=[null]) (C11,C22,C32,C42) --> (X="cat", stack=[])
- Compute the (maximum) number of tests
 CC-BY-NC-SA 4.0
CC-BY-NC-SA 4.0